On December 3, 2012 American Graphite Technologies entered into and executed a non-exclusive technology License agreement for patent and trade secret technology in the field of graphene oxide or “Bucky” paper. Pursuant to the terms of the agreement, we acquired the rights to further develop, commercialize, market and distribute certain proprietary inventions and know-how related to the manufacturing processes for graphene products, including graphene paper, also known as Bucky Paper.
"Graphene paper also known as “buckypaper” resembles carbon paper but don’t be fooled by the name. On its own, it looks like a mere thin "film like" paper and looks very fragile. However, this unassuming new “super paper” may revolutionize automobiles, aircraft, displays, electronics, batteries, medical treatments and more industries in years to come.
Graphene paper owes its physical qualities to a unique interlocking-tile lattice at the atomic scale. The material has exceptional stiffness and strength, due to the intrinsic strength of the two-dimensional graphene backbone and to its interwoven layer structure which helps to distribute loads. It also has intriguing electrical qualities because it is a zero band gap semiconductor. If Graphene oxide is used it is mechanically strong and electrically insulating.
Currently Graphene Paper is available only in limited sizes, it is relatively expensive and making it is very time consuming, American Graphite Technologies is working with Cheap Tubes Inc. and CTI Nanotechnologies LLC on developing a prototype production machine that makes Graphene Paper in larger and more affordable sizes than currently available.
Potential applications for Graphene paper include:
- Computer and television displays
- Electrical shielding
- Reinforcing Material for manufacturing cars, boats, airplanes and machinery
- Lightning Strike Dissipation
- Heat Dissipation
- Protection against electromagnetic pulses (EMP)
- Armor plating
- Reinforcement of plastics and polymers
- Electrodes for batteries, fuel cells, solar cells and capacitors
- Thermal heatsinks for electronic and computer equipment
- Artificial limbs
- Air and liquid filtration systems
-
Mining Assets
We are focused on acquiring mineral claims in geographical areas with proven reserves. The focus on areas with pre-proven claims allows us to utilize geological data to pin point exploration efforts.
LEARN MORE >>
-
Graphene
This "Miracle Material" is 200X stronger than steel, ultra thin, flexible and may one day replace silicone in computer chips
LEARN MORE >>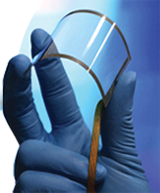
-
Graphite
Graphite demand is expected to increase by +50% by 2020. Demand from high tech applications is projected to be dramatic
LEARN MORE >>
-
 Latest News
Latest News- Queen's University and Eagle Graphite Announce Grant to Test Multi-Layered Graphene in Plastic Composites - Junior Mining Network June 2, 2017
- R&D Special Focus: Graphene - R & D Magazine May 31, 2017
- NextSource Materials' Modular Graphite Game Plan - InvestorIntel May 26, 2017
- Zenyatta Enters the Next Phase to Test Concrete Admixture ... - AZoNano May 26, 2017
- Graphene City: Research Hub Accelerates Innovation - R & D Magazine May 25, 2017